
Since December 2010, both methods have been applied to all patients after major hip surgery unless contraindicated. Since March 2010, this monotherapy has been augmented by IPC in some patients. We have routinely used low-dose aspirin (100 mg qd) in hip surgery patients. 13) Therefore, mechanical methods using intermittent pneumatic pumps have been gaining popularity, and variable results on their effectiveness have been reported in Asian countries. However, its use for Asian patients who have a relatively low VTE incidence has been controversial because of the bleeding risk. Resultantly, the use of chemoprophylaxis has increased. 5, 12) The two reports prompted interest in perioperative VTE and its prophylaxis in Asian surgeons, some of whom started to insist on aggressive prophylaxis using anticoagulants. 1, 10, 11) However, in 2005, two multicenter studies conducted in Asian countries reported that the incidence of postoperative VTE was not low in Asians, and it was consistent with that in Western countries. It has been considered that VTE occurs less frequently in Asians and surgeons have not recognized the necessity of perioperative prophylaxis.
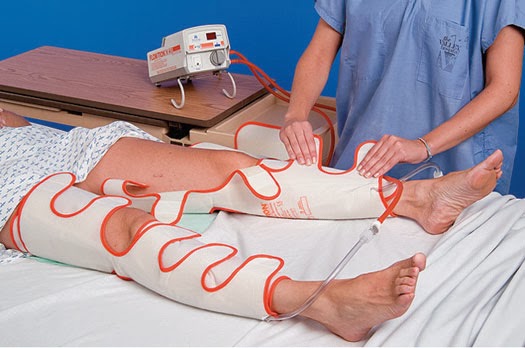
The American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) recommended mechanical methods alone primarily in patients at high risk of bleeding until the 8th edition of its guidelines. However, there have been debates on the efficacy of mechanical methods in VTE prevention. After surgery, these methods can be applied any time regardless of drain status. 9) Mechanical methods have no risk of unexpected bleeding and can be applied to the contralateral leg during operation.

4, 6)įor mechanical prophylaxis, graduated compression stockings and intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC) devices are used. 6, 8) Anticoagulants are very effective in VTE prophylaxis but have the risk of bleeding in the operation site and other sites such as intracranial and gastrointestinal sites. Newly developed anticoagulants such as low molecular heparin and factor Xa inhibitors (pentasaccharide) are widely used instead of heparin and wafarin. Chemical prophylaxis uses anticoagulants. 6, 7) There are two main categories of prophylaxis: chemical and mechanical.

5)īecause of the high incidence, rare but possible fatality, and subsequent post-thrombotic syndrome, active prophylaxis of VTE is strongly recommended in the perioperative period. 4) The incidence of VTE in Western countries after total hip arthroplasty (THA) without any prophylaxis is reported to range from 45% to 57%. 3) The injury of soft tissue including the vessel wall during operation and patient immobilization after a hip surgery are inevitable and known to increase the risk of VTE. 1, 2) PE occurs much less frequently than DVT, but it is a major cause of death after major hip surgery. Venous thromboembolism (VTE) comprising deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) is one of the major complications after major hip surgery.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
